In recent years, Europe has witnessed the rise of populist movements that have upended traditional political landscapes and challenged established institutions. Fueled by discontent and disillusionment, these movements have gained traction by capitalizing on socioeconomic anxieties, immigration concerns, and skepticism toward globalization. In this article, we will explore the impact and implications of the rise of populist movements in Europe, analyzing the underlying factors contributing to their growth and examining the potential consequences for the region’s political, social, and economic fabric.
Factors Driving the Rise of Populist Movements
Several factors have contributed to the rise of populist movements in Europe. Understanding these underlying drivers is crucial for comprehending the nature and appeal of these movements. Here are some key factors:
Economic Insecurity and Inequality
The lingering effects of the global financial crisis and subsequent economic hardships have created a sense of economic insecurity among many Europeans. Rising inequality, job insecurity, and stagnant wages have fueled resentment toward established political elites and mainstream parties.
Migration and Identity Concerns
Heightened levels of migration, particularly from conflict zones and economically disadvantaged regions, have sparked fears over cultural identity, social cohesion, and national security. Populist movements often exploit these concerns, tapping into anti-immigration sentiments and advocating for stricter border controls.
Euroscepticism and Loss of Sovereignty
A perception of diminishing national sovereignty and unease over the European Union’s influence on domestic affairs has resonated with certain population segments. Eurosceptic sentiments, fueled by concerns over losing control and decision-making power, have fueled support for populist movements.
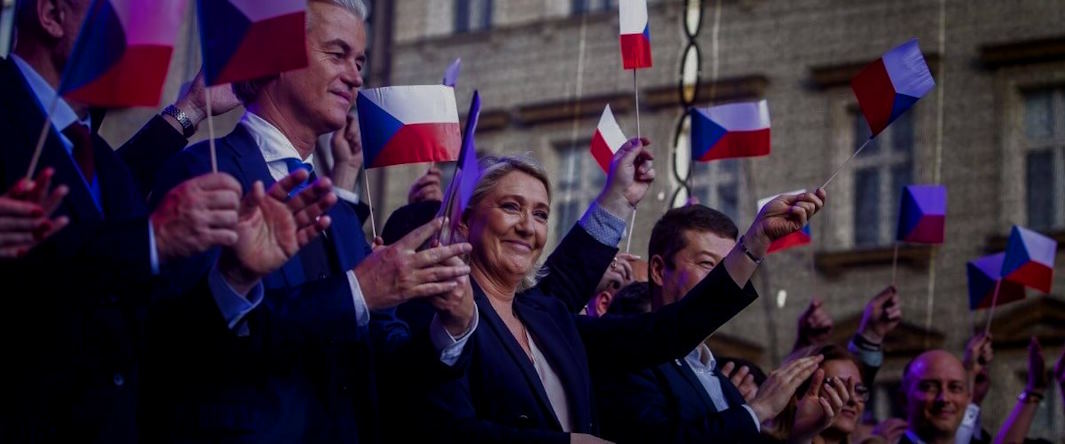

Impact of Populist Movements in Europe
The rise of populist movements has significantly impacted European politics, societies, and economies. Here are some key consequences:
Political Fragmentation
Populist movements have fragmented political landscapes, eroding the dominance of mainstream parties. It has led to the formation of coalition governments, political gridlock, and increased polarization, making achieving consensus and implementing effective policies more challenging.
Weakening of Institutions and Democratic Norms
Populist movements often challenge established institutions, including the judiciary, media, and civil society, undermining democratic norms and principles. Attacks on press freedom, erosion of checks and balances, and a disregard for the rule of law pose risks to democratic governance.
Social Divisions and Xenophobia
Populist rhetoric that scapegoats minority groups and promotes nativist ideologies has fueled social divisions and xenophobia. It can undermine social cohesion, strain intercommunity relations, and lead to the marginalization of vulnerable populations.
Economic Uncertainty and Trade Protectionism
Populist movements often advocate for protectionist measures and oppose free trade agreements. Such policies can hinder economic integration, disrupt supply chains, and undermine Europe’s position in the global economy, potentially leading to economic uncertainty and reduced growth prospects.
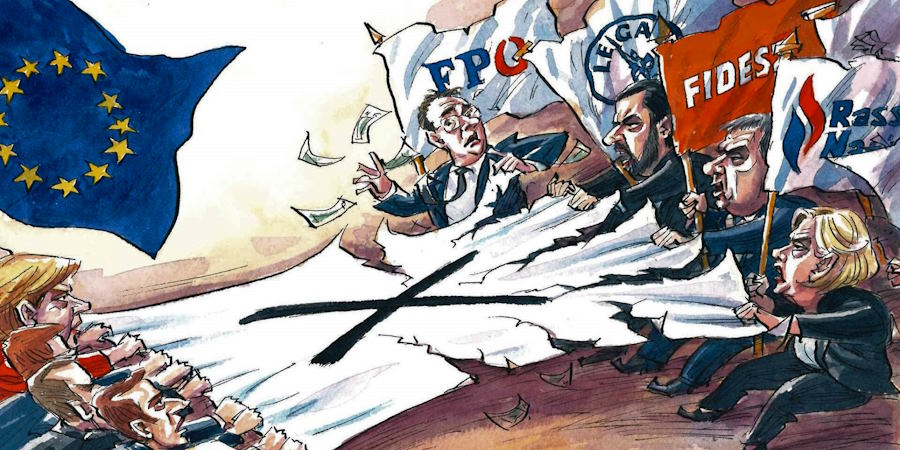

Implications for the Future
The rise of populist movements in Europe poses significant implications for the region’s future. Here are some key considerations:
Strengthening Democratic Resilience
Protecting democratic institutions, reinforcing the rule of law, and upholding democratic values are crucial to safeguarding Europe’s democratic resilience in the face of populist challenges.
Addressing Socio Economic Concerns
Tackling economic inequalities, improving social mobility, and addressing the root causes of economic insecurity are vital to alleviate the grievances that fuel populist movements.
Promoting Inclusive Policies
Embracing inclusive policies that address migration challenges, foster social cohesion, and promote cultural diversity can help mitigate the divisive narratives exploited by populist movements.
Engaging in Constructive Dialogue
Engaging in meaningful and constructive dialogues with citizens, including those who support populist movements, is essential. Understanding and addressing their concerns through evidence-based policies can help rebuild trust and bridge societal divides.
The rise of populist movements in Europe has profoundly impacted the region’s political, social, and economic landscape. Driven by various factors, these movements have disrupted traditional politics, challenged established institutions, and exacerbated social divisions. To navigate this complex scenario, it is crucial to address the underlying drivers, strengthen democratic resilience, promote inclusive policies, and engage in constructive dialogues.